Physics 12 Field and Force
Describe and interpret drawings of magnetic fields around permanent magnets and current-carrying wires Calculate the magnitude and direction of magnetic force in a magnetic field and the force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field Section Key Terms Magnets and Magnetization

Daily Life Examples and Practice Questions What's Insight
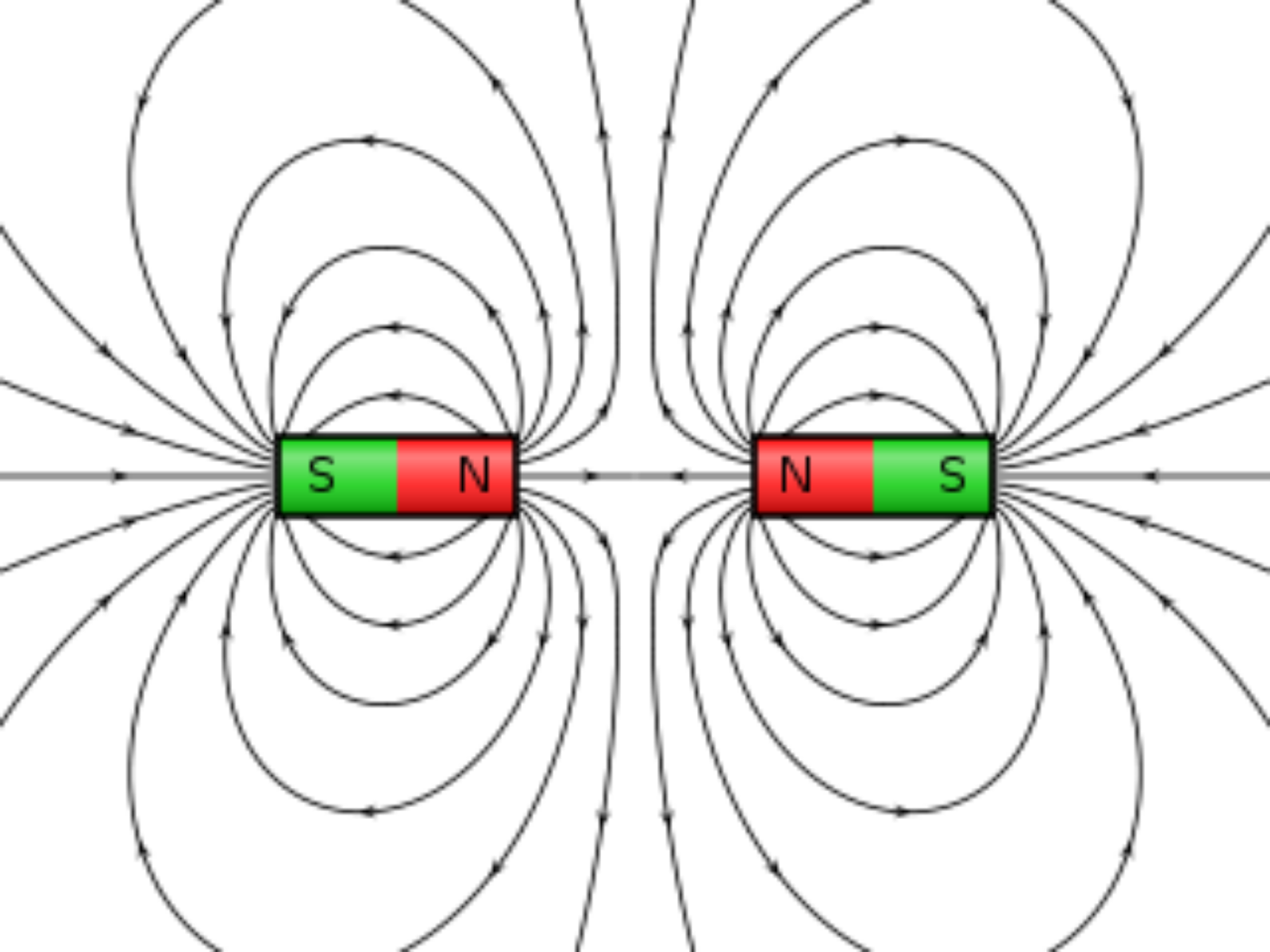
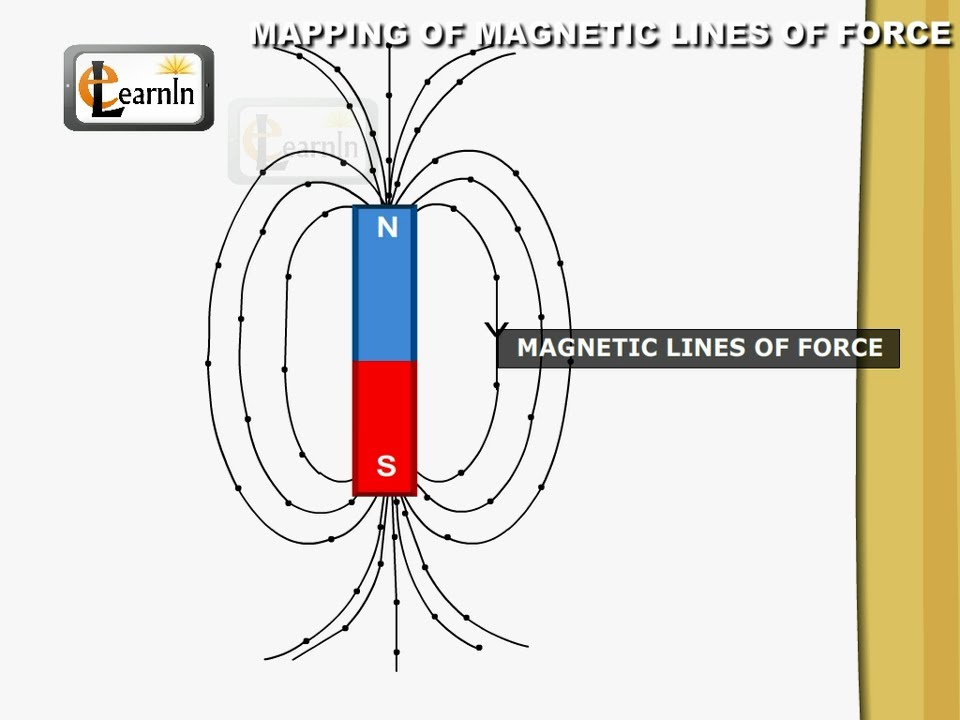
The magnetic field is an abstract entity that describes the influence of magnetic forces in a region. Magnetic field lines are a visual tool used to represent magnetic fields. They describe the direction of the magnetic force on a north monopole at any given position. Because monopoles are not found to exist in nature, we also discuss alternate means to describe the field lines in the sections.
Mapping of lines of force Elementary Science YouTube
Either moving a wire through a magnetic field or (equivalently) changing the strength of the magnetic field over time can cause a current to flow. How is this described? There are two key laws that describe electromagnetic induction: Faraday's law, due to 19ᵗʰ century physicist Michael Faraday.
The Field Lines Inside A Bar Go In What Direction? Explainer what happens
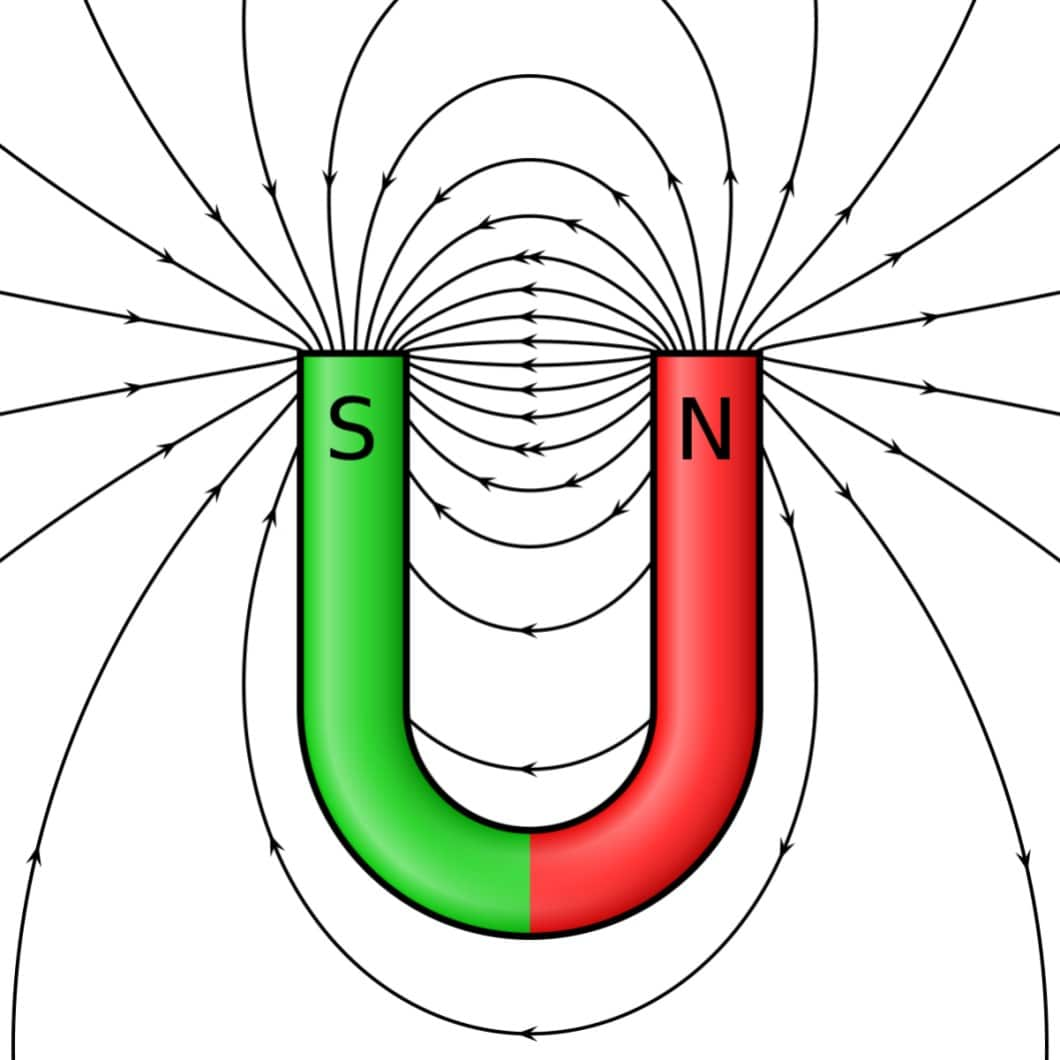
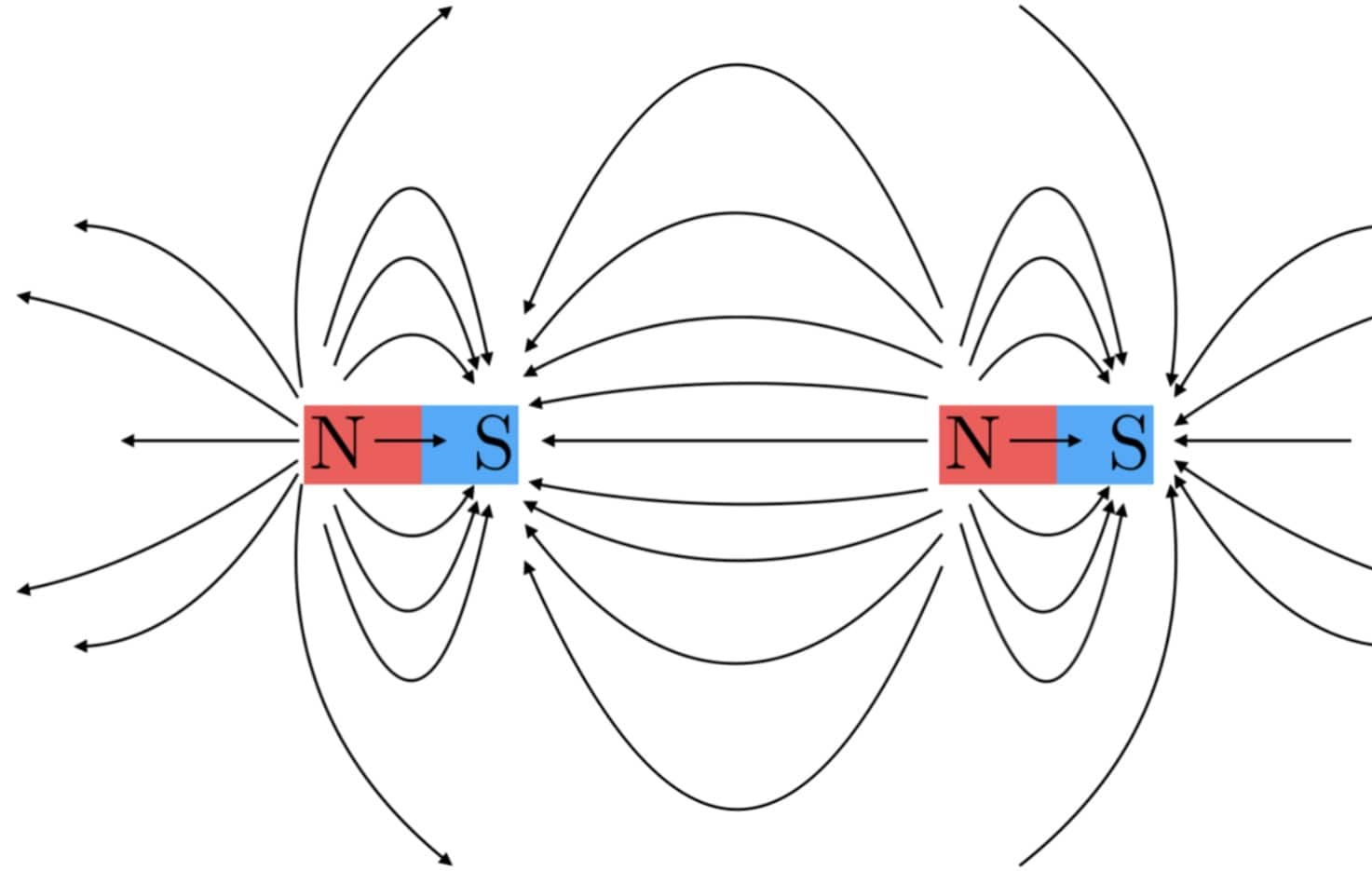
bar magnet diagram. A gallery of magnetic fields. Experiments with magnets and our surroundings. This page has several cool diagrams of magnetic fields. Studying these help give you a feel for how magnets actually interact with one another and with other objects. You will see that the fields can bend and move, and can even pop out of a magnet.
Bar diagram for education 1590918 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Magnets function as transducers, transforming energy from one form to another, without any permanent loss of their own energy. General categories of permanent magnet functions are: Mechanical to Mechanical - attraction and repulsion. Examples of applications that utilize this are magnetic separators, holding devices, magnetic torque drivers and.
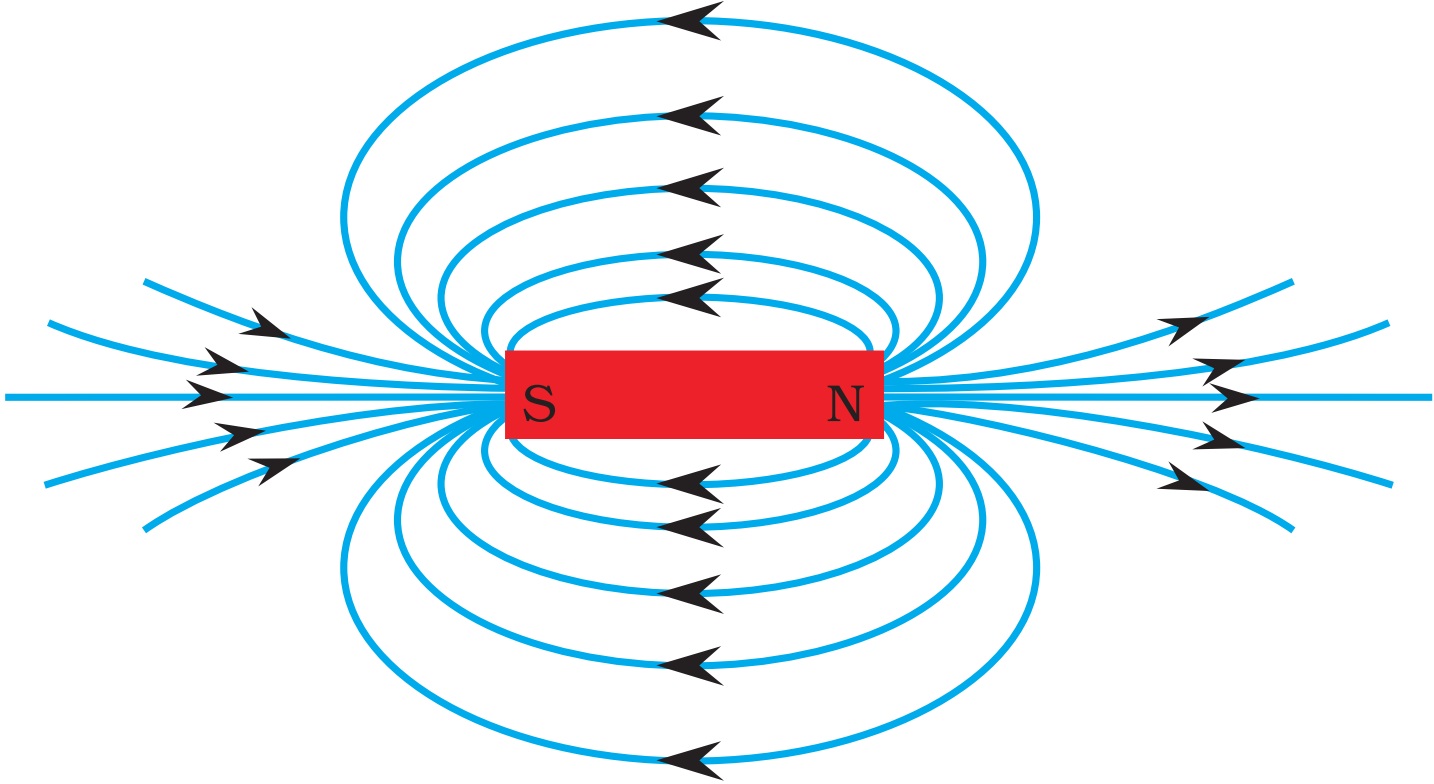
Field Lines Definition, Properties, How to Draw Teachoo
This page has several cool diagrams of magnetic fields. Studying these help give you a feel for how magnets actually interact with one another and with other objects. You will see that the fields can bend and move, and can even pop out of a magnet at places other that what you may expect to be the typical pole areas.
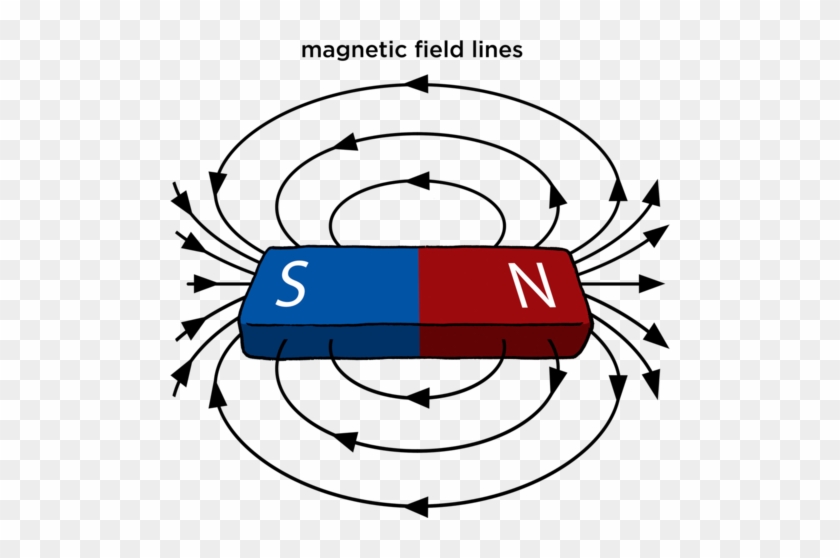
Labelled Diagram Of A Bar Free Transparent PNG Clipart Images Download
Question Video: Understanding the Magnetic Field of a Bar Magnet. The diagram shows a bar magnet. The bar magnet creates a magnetic field around it. At which point marked on the diagram is the magnetic field strongest? At which point marked on the diagram is the magnetic field weakest? 02:23.

Electrical Academia
Part 2: Constructing a Magnetic Field Diagram 2A: Parallel Magnets 1. Arrange two bar magnets and a series of compasses as pictured here: 2. Sketch the compass needles' directions in the diagram. Based on these compass directions, sketch in some field lines. Question 2: Is there any place in this region where the magnetic field is zero? If so.

Learn about Science for Kids science, Science words, Teaching science
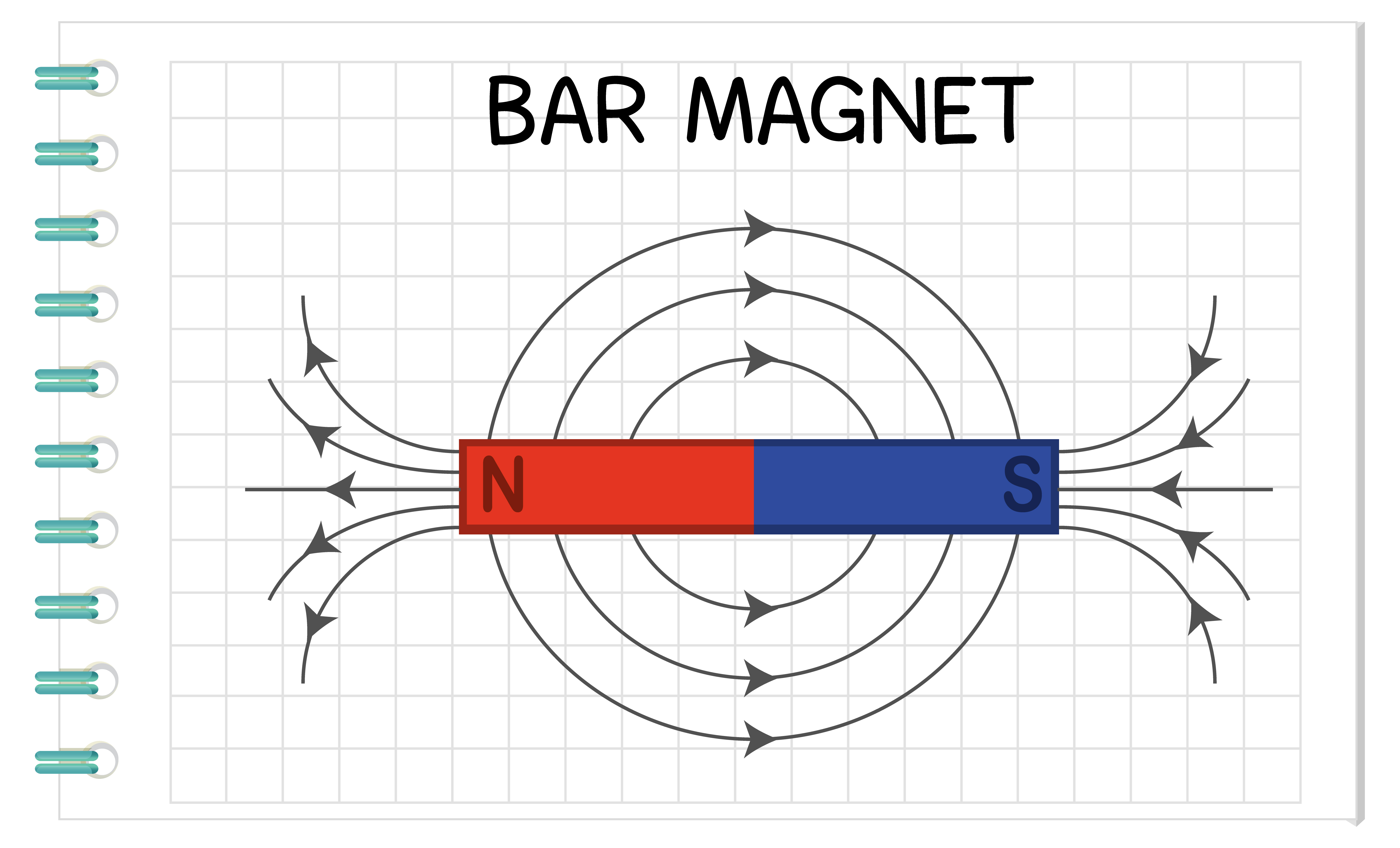
The strongest external magnetic fields are near the poles. A magnetic north pole will attract the south pole of another magnet, and repel a north pole. The magnetic field lines of a bar magnet can be traced out with the use of a compass. The needle of a compass is itself a permanent magnet and the north indicator of the compass is a magnetic.
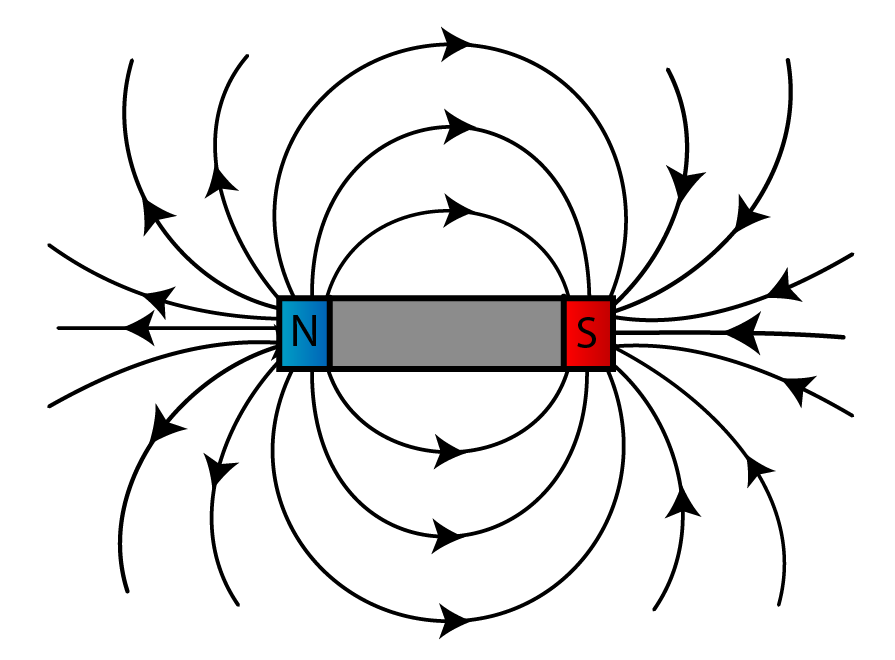
Introduction to (Revision) SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes
A further difference between magnetic and electric forces is that magnetic fields do not net work, since the particle motion is circular and therefore ends up in the same place. We express this mathematically as: W = ∮B ⋅ dr = 0 (21.4.5) (21.4.5) W = ∮ B ⋅ d r = 0.
How it works Diagram — How work diagram (Cross section)
The magnetic force is directed where your thumb is pointing. If the charge was negative, reverse the direction found by these steps. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: Magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges. The direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge is perpendicular to the plane formed by b v. ⃗.
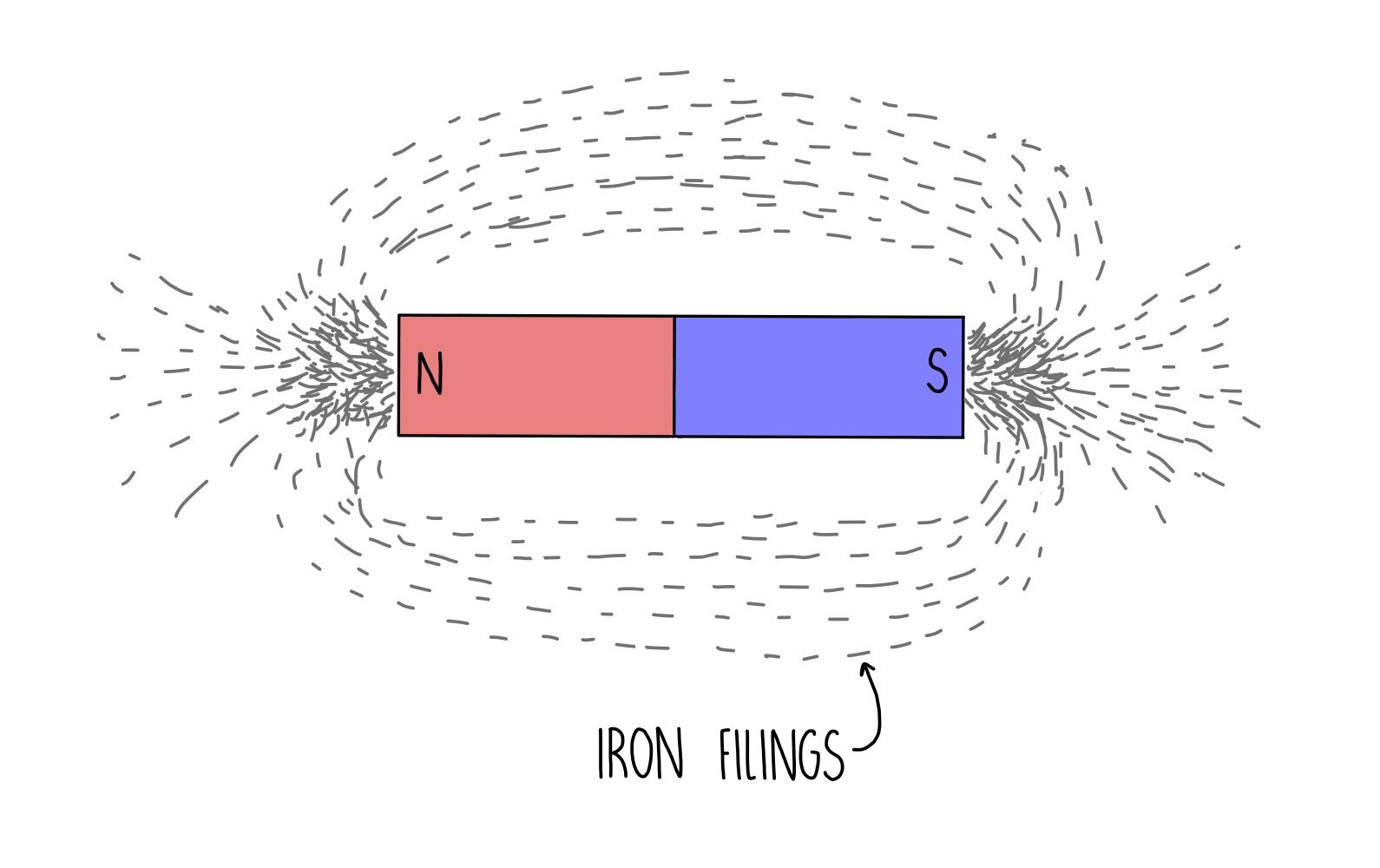
(GCSE) — the science hive
F = qvBsinθ F = q v B sin θ. 11.2. where θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field. The SI unit for magnetic field strength B is called the tesla (T) after the eccentric but brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla (1856-1943), where. 1T = 1N A ⋅ m. 1 T = 1 N A · m.
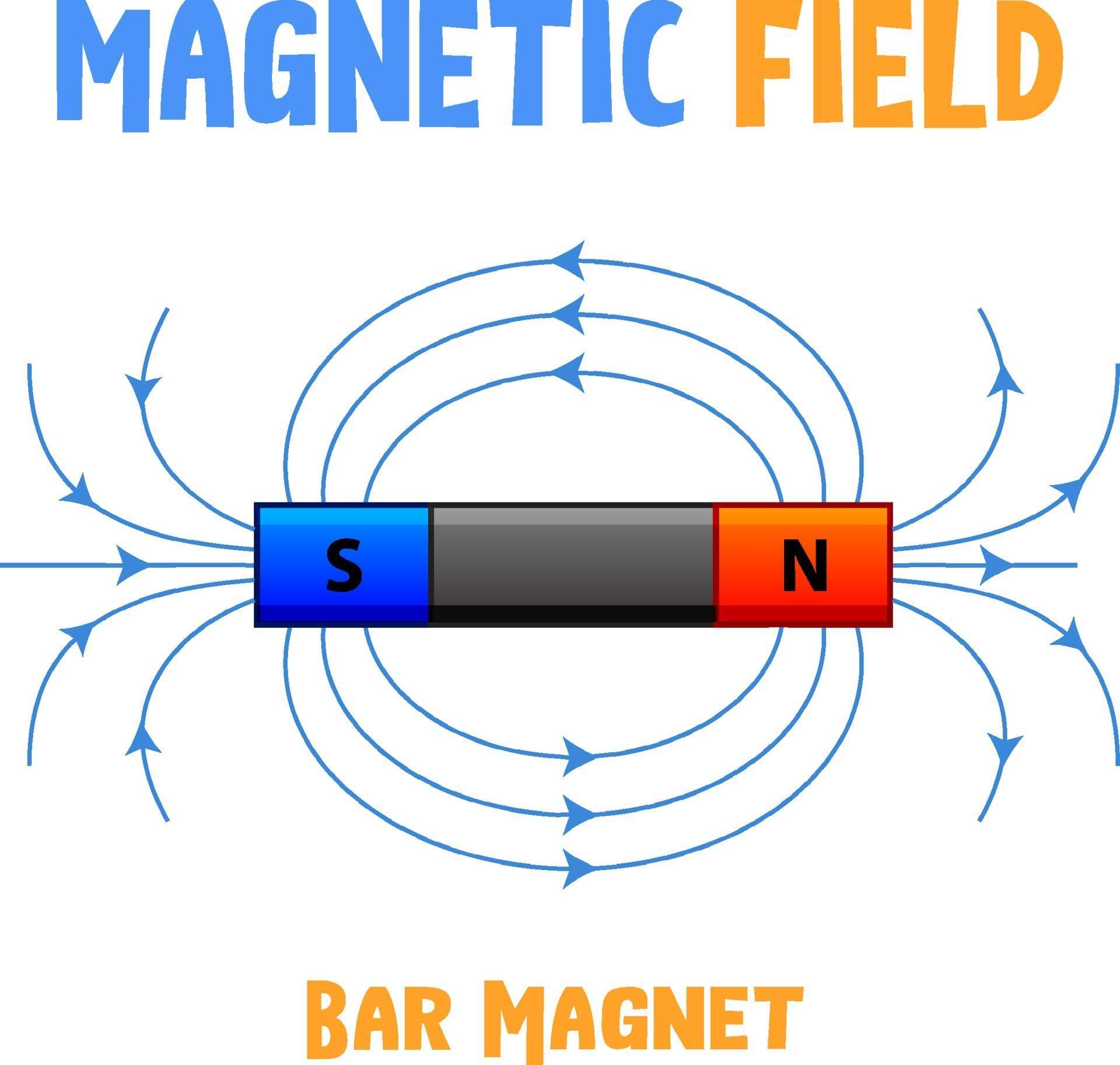
field of bar 2062901 Vector Art at Vecteezy
A magnet is any object that can attract other materials with magnetic properties through a magnetic force. Every magnet has a north pole and a south pole. Either pole will attract iron. The direction of magnetic force between two magnets depends on how the poles are oriented. Opposite poles attract Like poles repel
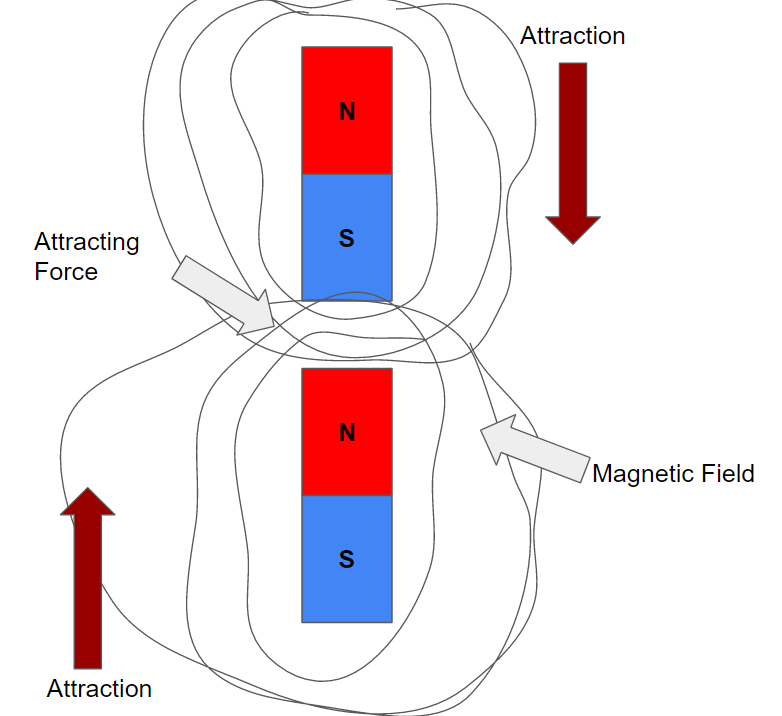
Spectacular Science
This drawing shows a cross section through the center of the coil. The crosses are wires in which current is moving into the page; the dots are wires in which current is moving up out of the page. An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current.
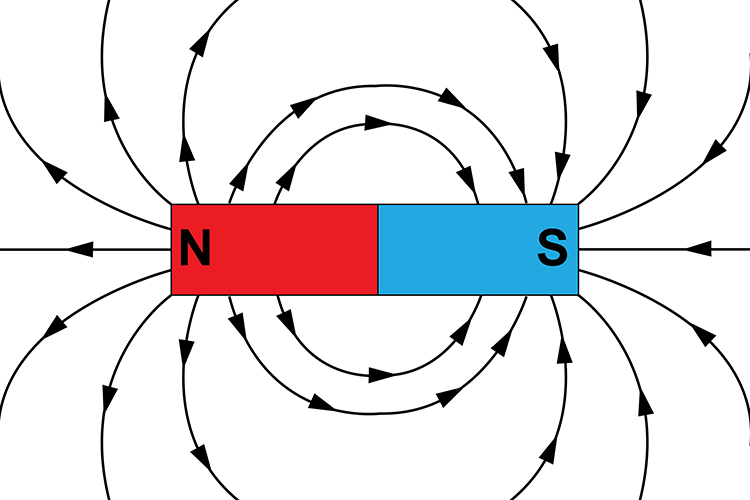
Remember which way field lines on a travel
The basic process of generating currents with magnetic fields is called induction; this process is also called magnetic induction to distinguish it from charging by induction, which uses the electrostatic Coulomb force. When Faraday discovered what is now called Faraday's law of induction, Queen Victoria asked him what possible use was electricity.
Bar What is Bar Uses and Properties of Bar
An electromagnet is a coil of wires that becomes a magnet when electric current runs through it. Electromagnets only work when the electric current is turned on. Increasing the electric current or increasing the number of wire loops increases the strength of the electromagnet.